Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse (ADW) is one of the so-called DB as a Service (DBaaS) or probably we should call it Data Warehouse as a Service (DWaaS) with the difference that this service is completely automatic and autonomous.
This service is comprised by an Oracle Database (of course) already pre-configured for analytics, data lakes and data warehouse workloads. This Oracle Database (PDB) has 18c features running on Exadata hardware. Oracle Exadata software is 18c with features like In-Memory delivered from the cell server.
There’s a service console that helps to manage the ADW services.
On top of this, Machine Learning (ML) tools help with data analysis and data models. Development tools like SQL Developer are useful to create objects, load data and more.
Let’s now talk about tasks that happen automatically:
Automatic statistics gathering during direct-path load operations
Automatic tuning
Automatic Partitioning
Automatic In-Memory
Automatic Indexing (soon)
Automatic Compression
Automatic Tablespace Management
Automated backups and patching
ADW is also capable of repair itself. Machine Learning is used to detect anomalies and uses pattern recognition to determine if this problem is already in the problem knowledge-base. If is a known problem, it will apply the fix automatically.
On the security side all the information is encrypted at rest. This means that backups and all data in the tablespaces is encrypted using TDE.
The connectivity between ADW and the rest of the world is secured be default. Oracle provides a wallet file that contains all the connectivity information required to login.
If you open this file you’ll notice that all connectivity is being done through SSL.
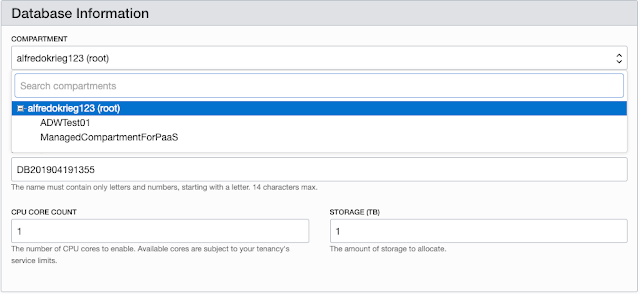
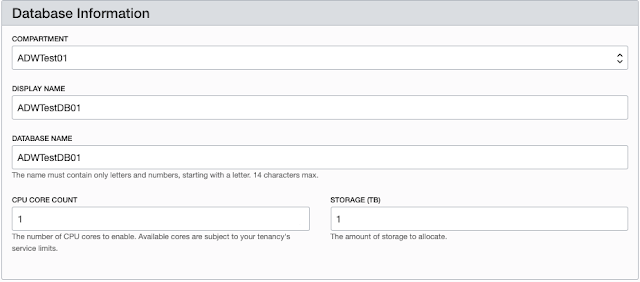
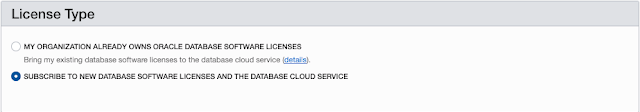
(security=(ssl_server_cert_dn=… Provisioning is quite easy using the service console. From the main dashboard you can click on “Create a data warehouse” button.